What Size Generator Do You Need For Your House?

Selecting the appropriate generator size for your home is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient power during outages. A generator that is too small won’t support all your essential appliances, leaving you in the dark when you need power the most. On the flip side, an oversized generator can lead to unnecessary expenses and wasted energy. This guide will help you understand the importance of choosing the right generator size for your home, the key factors to consider, and how to ensure your investment provides the security and peace of mind you deserve during unexpected power interruptions.
Understanding Generator Sizing and Its Significance
Generator sizing involves determining the right power capacity, measured in watts, to support your household’s essential appliances during an outage. This includes both the starting and running wattages of your appliances and systems. To determine the appropriate size for your whole-home generator, start by calculating the total wattage of all critical appliances and systems you need to power during an outage, such as refrigerators, HVAC systems, lights, and medical equipment.
Overview of Watts, Kilowatts, and Their Relation to Generator Size
Watts and kilowatts are units of power measurement that indicate the electrical capacity of a generator. Understanding these terms is essential for making an informed decision about generator size.
- Watts (W): The basic unit of power. Small household appliances typically use watts to denote their power requirements.
- Kilowatts (kW): Equivalent to 1,000 watts. Larger appliances and overall household power needs are often measured in kilowatts.
How to Calculate the Watts Needed for a Whole-Home Generator
When choosing a whole-home generator, one of the most important steps is determining how many watts you need to keep your home running smoothly during a power outage. Follow these steps to calculate the necessary wattage for your generator:
Step 1: Identify Essential Appliances and Devices
Start by making a list of all the appliances and devices you want to keep running during an outage. These typically include:
- Refrigerator
- Freezer
- Air conditioning or heating system
- Lights
- Kitchen appliances (microwave, oven, stove)
- Washer and dryer
- Water heater
- Well pump (if applicable)
- Electronics (TV, computer, chargers)
- Medical equipment (if needed)
Step 2: Determine the Starting and Running Watts
Each appliance has two power ratings: starting watts (the initial surge of power needed to start the appliance) and running watts (the power needed to keep the appliance running). You can find these ratings in the appliance manual or on the manufacturer’s website. Here are some typical examples:
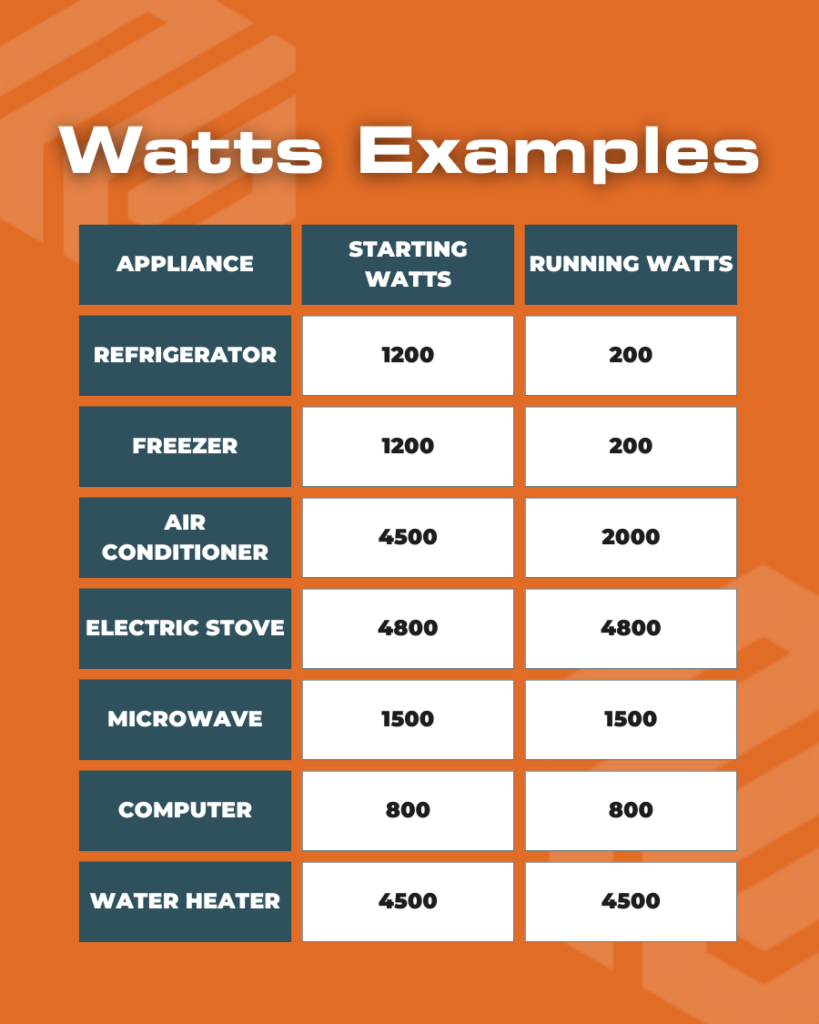
Step 3: Calculate Total Wattage
Add up the running watts of all the appliances you want to power. Next, add the highest starting watts of any single appliance. This ensures that your generator can handle the initial power surge required to start your most demanding appliance while running everything else.
In the example below, it would be:
4500 Watts (running Watts of all appliances) + 4500 (starting Watts of the air conditioner) = 9000 Watts.

In the example above, you would need a generator that can handle at least 9000 watts to cover both the running and starting power requirements of your essential appliances.
Step 4: Choose a Generator with a Suitable Wattage
Once you’ve calculated the total wattage, choose a generator that meets or exceeds this number. It’s a good idea to select a generator with a slightly higher wattage than your calculation to account for any additional appliances or devices you may need to power in the future.
Step 5: Consult with a Professional
Calculating the exact power needs for your home can be complex, especially with unique appliances or specific power requirements. Our Power Consultants at Premier Generators can help ensure you choose the right generator size and avoid potential issues.
Key Considerations for Choosing the Right Generator
When selecting a generator, several factors come into play:
- Fuel Type: Options include propane and natural gas. Propane burns cleaner and has a longer shelf life but requires a separate tank. Natural gas is convenient if you already have a gas line but may not be available in all areas.
- Fuel Availability and Storage: Ensure you have access to your chosen fuel type and a safe storage solution. Propane has specific storage requirements, while natural gas needs existing gas lines.
- Runtime and Fuel Efficiency: A generator with a longer runtime is crucial for extended power outages. Fuel efficiency impacts your choice as well, with high-efficiency models using less fuel, reducing refueling frequency, and lowering operational costs.
Balancing these factors will help you select a generator that meets your needs effectively.
Installation Requirements for Standby Generators
Proper generator installation is crucial for the effective and safe operation of your standby generator. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Location and Placement: Install the generator on a stable, level surface, ideally 5-10 feet away from your home to avoid carbon monoxide exposure and noise issues. Ensure it’s in a well-ventilated area, away from vents and doors.
- Electrical Considerations: A transfer switch is necessary to safely connect the generator to your home’s electrical system and prevent backfeeding. Ensure all wiring complies with local electrical codes and consider having a licensed electrician handle the installation.
- Fuel Supply and Exhaust: Choose a location that accommodates the fuel type of your generator—natural gas, propane, or diesel—and ensures proper exhaust venting to avoid fumes entering your home.
- Permits and Inspections: Check local regulations for required permits and schedule an inspection to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Maintenance and Accessibility: Ensure the generator is placed where it’s easily accessible for maintenance, with adequate clearance around it as specified by the manufacturer.
Hiring a professional for installation is highly recommended to ensure all requirements are met, providing you with reliable and efficient power when needed.
Long-Term Operating and Maintenance Costs: What You Need to Know
Investing in a whole-home generator involves more than just the initial purchase price. To ensure your generator remains a dependable power solution for years to come, it’s essential to factor in long-term operating and maintenance costs. While a high-quality generator can offer peace of mind during power outages, budgeting for ongoing expenses is crucial.
Routine Maintenance Requirements
Routine generator maintenance plays a critical role in the reliability and longevity of your generator. Like any piece of machinery, your generator requires regular upkeep to perform optimally. This maintenance includes systematic checks and replacements of vital components such as oil, filters, and batteries. Neglecting these tasks can lead to decreased efficiency, unexpected breakdowns, and costly repairs.
To maintain your generator’s performance:
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are necessary, typically every 100-150 hours of operation or annually, to keep the engine running smoothly.
- Air and Fuel Filters: Air filters should be replaced every 6-12 months, while fuel filters need to be changed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Routine Inspections: Regular checks of the battery, coolant levels, and connections are essential to catch potential issues early.
By understanding and planning for these maintenance needs, you can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems and ensure your generator is always ready to provide power when you need it most. Proper upkeep helps avoid unexpected breakdowns and keeps your generator a reliable source of power, making it a smart investment in the long run.
Conclusion
Assessing your power needs carefully helps avoid the pitfalls of undersizing or oversizing your generator. By understanding your specific requirements and consulting with experts, you can choose a generator that delivers reliable performance and long-term value. For personalized guidance and expert advice, contact our Power Consultants at Premier Generators. Our team is here to provide the information you need to make a smart investment in your whole-home generator, ensuring peace of mind during any power outage!