What Is a Standby Generator?

A standby generator is a permanent power backup solution that automatically steps in when your main power goes out. Unlike portable generators, it’s connected directly to your home’s electrical panel and fuel line, allowing it to provide continuous power for essential or entire home functions without manual setup or refueling.
- How It Works: The generator connects to your home’s electrical panel through a transfer switch. When power goes out, the switch detects the failure, starts the generator, and seamlessly supplies electricity to essential circuits or even your entire home.
- Fuel Source: It typically runs on natural gas or propane, meaning there’s no need to refill it manually. This fuel connection allows the generator to run continuously during prolonged outages, unlike portable models that rely on gas refills.
Why Choose a Standby Generator?
Standby generators keep key systems—heating, cooling, refrigeration, and security—up and running in a power outage.
This system is also a long-term investment in home value, offering peace of mind and convenience by ensuring power is there when you need it most.
Schedule an estimate with us to see how a standby generator can keep your home safe and functional, no matter the circumstances.
How Does a Standby Generator Work?
A standby generator operates with minimal involvement from the homeowner, thanks to an automated system that quickly responds to power outages. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- Power Monitoring: The generator is constantly connected to your home’s electrical panel via a transfer switch, which monitors the main power supply. As soon as an outage is detected, the generator is triggered to start.
- Automatic Transfer Switch: This switch disconnects the house from the utility line to prevent backfeeding and damage. It then seamlessly connects the generator to your home’s circuits, allowing electricity to flow from the generator instead.
- Power Restoration: Within seconds, the generator takes over and powers essential or all home circuits, depending on its capacity and setup. When the main power returns, the transfer switch reconnects to the utility grid and shuts down the generator.
- Fuel Source: Standby generators run on a steady fuel supply, usually natural gas or propane, allowing them to operate for extended periods without the need for refueling.
This automated system provides a reliable, “set it and forget it” approach to power continuity, keeping essential functions in your home running smoothly during an outage.
Types of Standby Generators
Standby generators come in a range of sizes and capacities, tailored to different power needs and settings. For homeowners, choosing the right type of standby generator means understanding the options available and selecting one that can comfortably power essential circuits or the entire house. Here’s a breakdown of the main types and considerations for residential standby generators.
1. Residential vs. Commercial Standby Generators
- Residential Generators: These are designed specifically for homes, delivering enough power to keep lights, heating/cooling systems, and essential appliances running during an outage. They are typically available in a range of output capacities from around 7 kW to 26 kW, which is sufficient for most single-family homes.
- Commercial Generators: Though not typically necessary for residential use, commercial standby generators are built to support larger power demands, like those in office buildings, hospitals, or industrial settings. They start at around 25 kW and can go up to several hundred kW. These units are more heavy-duty, often requiring three-phase power connections, and are engineered to handle intensive, constant loads.
2. Standby Generators by Power Output
Residential standby generators are generally available in the following power ranges, each serving different household requirements:
- 7-12 kW: Suitable for smaller homes or for running essential circuits only, such as lights, refrigerator, sump pump, and possibly a small heating/cooling system. This is a budget-friendly option if full home power is not necessary.
- 12-20 kW: Ideal for medium-sized homes, providing enough power to keep a few more systems running comfortably. These generators can typically support major appliances, lights, and HVAC systems in most homes.
- 20-26 kW: This range is popular for whole-house coverage in larger homes. These units can power most of the home’s electrical needs, including major systems like HVAC, kitchen appliances, and other household devices.
3. Fuel Type Options
The fuel type for your standby generator impacts its performance, availability, and long-term maintenance. Residential standby generators typically use one of the following fuel sources:
- Natural Gas: This is a popular choice for its steady supply through utility lines, eliminating the need to refill the fuel tank manually. Natural gas burns cleanly, making it an efficient and low-maintenance option for extended use.
- Propane: Propane-powered generators are another reliable choice, particularly in areas without natural gas access. Propane is stored in an on-site tank, which means the generator will continue running as long as the tank is sufficiently full. Propane burns cleanly as well, though it may require regular refills depending on generator usage and tank size.
Both natural gas and propane offer advantages in terms of longevity and reliability, especially compared to gasoline, which is typically reserved for portable generators and requires frequent refilling and careful storage.
Key Components of a Standby Generator System
A standby generator relies on a few essential parts that work together to deliver reliable backup power. Here’s what makes it all tick:
1. Engine – This is the core of the generator, where fuel (usually natural gas or propane) is converted into mechanical energy to drive the alternator. It’s built to handle long runs, so it’s ready to go whenever the power cuts out.
2. Alternator – Converts the engine’s mechanical energy into electricity. Good alternators provide steady, clean power, which helps protect your appliances from surges or fluctuations.
3. Control Panel – Acts as the generator’s brain. It monitors utility power and automatically starts the generator when it detects an outage. The control panel also handles self-testing, alerts, and remote monitoring if you’ve got that setup.
4. Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) – Disconnects your home from the utility grid when the generator kicks in and reconnects once the grid power’s back. It’s a critical safety feature to prevent backfeeding and potential damage.
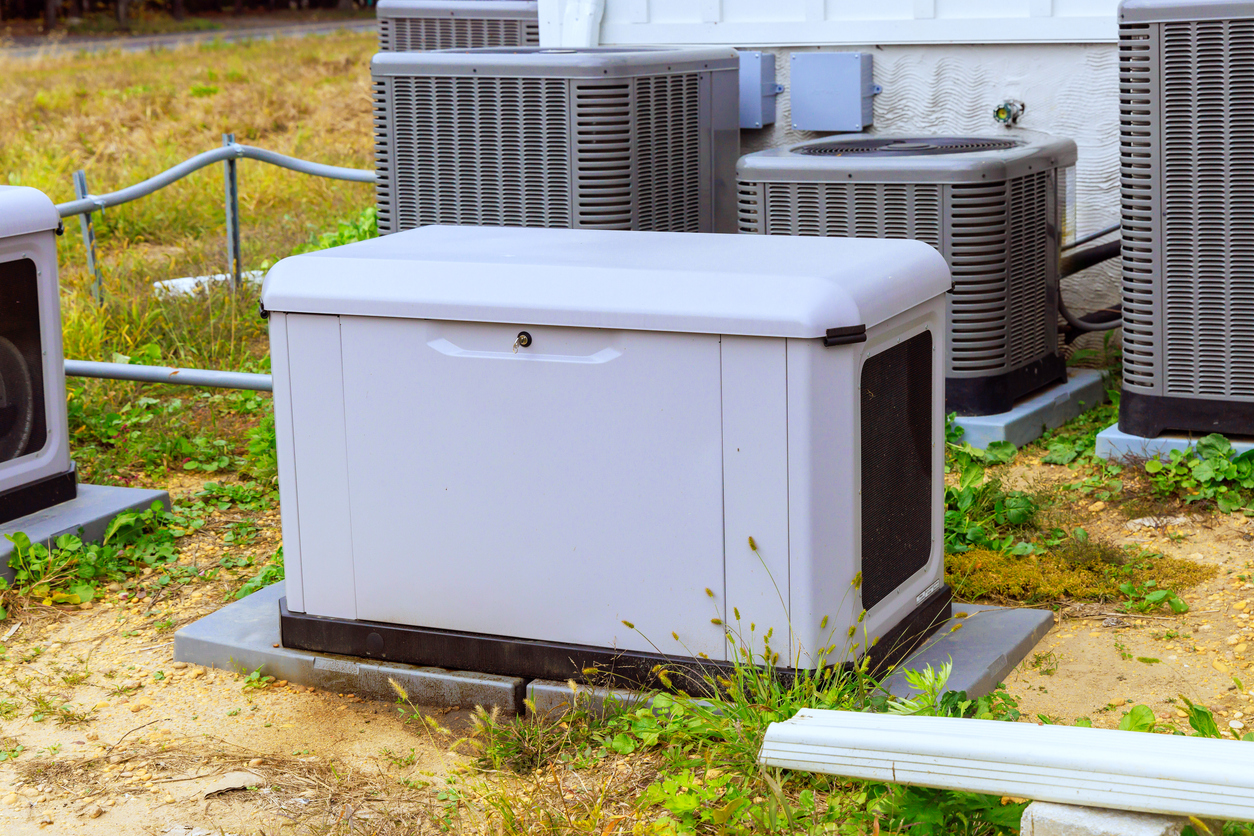
5. Enclosure – A tough, weatherproof shell that protects the generator’s guts from the elements. It also helps with sound insulation, keeping noise down during operation.
6. Fuel System – Ensures a steady supply of fuel to the engine, either from a natural gas line or an on-site propane tank. This setup lets it run for as long as you need without constant refueling.
7. Battery and Charger – The battery starts the engine, and an onboard charger keeps it powered up and ready. No charged battery, no start-up.
8. Cooling and Exhaust System – Keeps the engine cool and directs fumes safely away, preventing overheating and maintaining safe operation during longer runs.
Benefits of a Standby Generator for Homes
Automatic, Reliable Power
Standby generators can start automatically during an outage, keeping essential systems like heating, cooling, and security active without manual setup.
Protection During Severe Weather
Standby generators are invaluable in areas hit by hurricanes and storms, where long outages are common. When the power fails, they step in instantly, keeping your home safe and comfortable through extended blackouts—a true lifesaver in storm-prone regions.
Safety and Security
A standby generator keeps lights, communication devices, and security systems running, adding a layer of safety during emergencies.
Boosted Home Value
Having a backup generator is a strong selling point, especially in areas with frequent outages, making your home more appealing and potentially raising its value.
Low Maintenance
Many standby generators are designed for minimal upkeep, and some models even perform automatic self-tests to ensure reliability. For added convenience and peace of mind, we offer a maintenance and monitoring service to keep your generator in top shape, handling routine checks and servicing for you.Consistent Fuel Source
Standby generators typically use natural gas or propane, giving them a stable fuel supply for extended use during long outages, unlike gasoline which requires frequent refills.